Improving a Good Website Structure
Improving a good website structure Many websites, such as websites or blogs, have a confusing structure. Content is often haphazardly linked and the user journey is full of dead ends and strange paths. This can be frustrating for your visitors and difficult for Google to index.
In this post we will provide tips to guide you through strategies to improve the structure of your website, which can help you improve your search rankings and increase revenue from the same number of visitors. If you are serious about developing a website or blog for your business needs, read on this post to the end!
What is website structure?
Website structure is how the different pages on your site are linked to each other using internal links and their hierarchy. This is how the information on your site is organized and presented so that the algorithm can read the context well. A good website structure facilitates easy navigation for users and crawlers which improves the SEO ranking of your website in search engines.
So the role of a designer is to create a website that has a great UX that maintains accessibility and is easy to use. A good website structure improves the usability or user-friendliness of your website by making it easier for users to find what they are looking for. To structure a website, you need to map out how you will organize the content on your site (homepage, categories, individual pages, blog posts). This is why structuring a website like a website or blog should be the first step in any web design project.
How to Improve Website Structure
The structure of your website is like the architectural plan of a building. It provides an outline of how your posts and pages are linked together. It also takes into account the links you place in your menus. When Google indexes a site, it follows these links to create your sitemap.
User flow, on the other hand, is all about how people browse your site. The structure of your website will play a big role in this. Other factors like how you tag those links and the quality of your content also come into play.
A website structure that functions as a wrapper for components or other website elements is to improve a good website structure, you usually need to do one or more of the following:
Improve your URL structure
Make the site easier to navigate
1. Improve your URL structure
An easy-to-understand URL will convey content information more easily to the Google search engine. Creating descriptive categories and filenames for website documents not only helps your site stay better organized, it can also cause search engines to crawl your documents better. It will also make URLs easier and "friendly" for those who want to link to your content. Visitors may be annoyed by very long and hidden URLs containing few recognizable words.
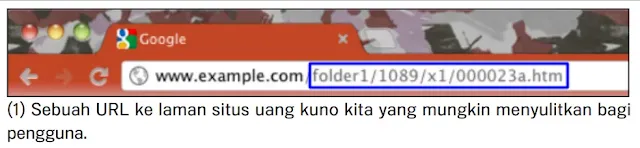
URLs like the one in the image above can be confusing and unfriendly. Users will have a hard time quoting URLs from memory or creating links to URLs. Users may also believe that some URLs are unimportant, especially if the URLs show many unrecognizable parameters. They may omit part of the URL so that the link becomes broken.
Some users may link to your page using the page URL as the link text. If the URL contains relevant words, it will provide users and search engines with complete information about the page rather than what the ID or odd-named parameter gives. A good URL you can see as in the image below.
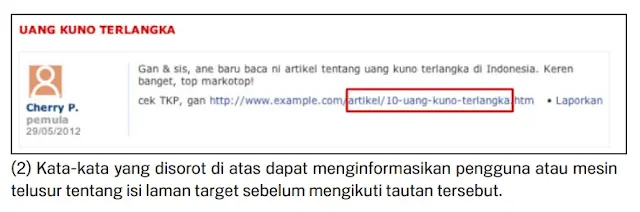
URLs are displayed in search results, remember that URLs in documents are shown as part of search results on Google, below the title and snippet of the document. Like titles and snippets, words in URLs in search results will appear bold when they appear in a user's query.
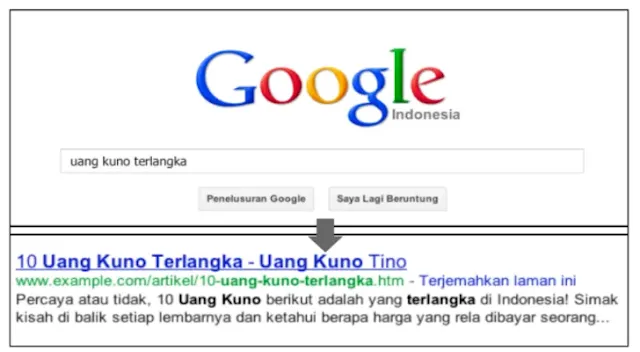
In the image above is another example showing the URL in our domain for a page containing articles about the rarest ancient coins. Words in URLs may be more attractive to searchers than ID numbers like "www.example.com/article/102125/".
Google is good at crawling all kinds of URL structures, even if the URLs are quite complex, but it's worth taking the time to make your URLs as simple as possible for users and search engines. Some webmasters try to achieve this by rewriting dynamic URLs to static URLs; Google has no problem with this, but we want to remind you that this is an advanced procedure and if done incorrectly, can result in search problems with your site. To learn more about URL structure, we recommend the Webmaster Help Center page for creating Google-friendly URLs.
Choose a URL that is easy for users and search engines to understand, There are 3 best practices that we recommend as follows:
Use words in URL
URLs with words that are relevant to the content and structure of the site will be more friendly to visitors navigating your site. Visitors remember the URL better and may be more interested in linking to it.
Avoid:
- Using long URLs with unnecessary parameters and session IDs
- Choose a generic page name like "page1.html"
- overusing keywords like "ancient-money-ancient-money-ancient-money.htm"
Create a simple directory structure
Use a directory structure that organizes your content well and makes it easy for visitors to know where they are on your site. Try using your directory structure to indicate the type of content found at those URLs.
Avoid:
- Creating deep nested subdirectories like ".../dir1/dir2/dir3/dir4/dir5/dir6/page.html"
- Using a directory name that is not related to the content in it
Provide one version of the URL to reach the document
To prevent users from linking to one version of a URL and other users linking to another (this can damage the reputation of the content in the URL), stay focused on using and referring to one URL in your internal linking and page structure. If you find that people are accessing the same content via multiple URLs, setting up a 301 redirect from the disliked URL to the dominant URL is a great solution for this. You can also use the canonical URL or use the rel="canonical" link element if you can't redirect.
Avoid:
- Have pages from subdomains and root directories that access the same content. For example: "domain.com/page.htm" and "sub.domain.com/page.htm"
- Uses odd URL capitalization - many users like lowercase URLs and remember them better
2. Make the site easier to navigate
Website navigation is important in helping visitors find the content they want quickly. It can also help search engines understand what content webmasters find important. While Google search results are provided at the page level, Google also wants to capture the role of a single page for the entire site.
Plan your navigation based on your homepage All sites have a homepage or "root" page, which is usually the site's most visited page and the starting point of navigation for many visitors. If your site has only a few pages, you should think about how visitors move from your general page (root page) to pages that contain more specific content. Do you have enough pages around a specific topic area that it would make sense to create a page that describes these related pages (eg root page -> related topic listing -> specific topic)? Do you have hundreds of products.
Ensure more convenience for users using 'breadcrumb lists'. Different that need to be classified in multiple categories and sub-category pages?
A breadcrumb is a row of internal links at the top or bottom of a page that allows visitors to quickly navigate back to the previous section or to the root page.
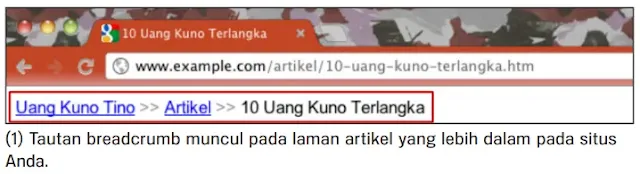
Many breadcrumbs have the most general page (usually the root page) as the first and far right link and load the more specific sections out on the right side.
Website navigation structure To make the site easier to navigate. Here's how to make your site easier to navigate:
Create a natural flowing hierarchy
Make it as simple as possible for users to open the general content and the specific content they want on your site. Add navigation pages if necessary and effectively incorporate these additions into your internal linking structure.
Avoid:
- Creating a complex web of navigation links, for example linking every page on your site to every other page
- Too passionate about dissecting your content (so it takes twenty clicks)
Uses a lot of text for navigation
Controlling most of the page-to-page navigation on your site via text links will make it easier for search engines to browse and understand your site. Many users also like this approach over the others, especially for devices that may not handle Flash or JavaScript.
Avoid:
- Have navigation based entirely on drop-down menus, images, or animations - most, but not all, search engines can find such links on a site, but if a user can navigate to all pages in the site via normal text links, then this will increase the accessibility of your site; more in how Google handles non-text files.
For navigation, the focus should be on simplicity and user-friendliness!
Put an HTML sitemap page on your site, and use an XML sitemap file
A simple sitemap page with links to all of the most important pages or pages (if you have hundreds or thousands of pages) on your site can be useful. Creating an XML Sitemap file for your site helps ensure that search engines find the pages on your site.
Avoid:
- Leaving your HTML sitemap pages obsolete with broken links
- Create an HTML sitemap that simply lists pages without organizing them, for example by subject
Has a useful 404 page
Users sometimes come to pages that aren't on your site, either by following a broken link or typing the wrong URL. By having a custom 404 page that can guide users back to the actual page on your site, users will have a much better user experience. Your 404 page should probably have a link back to the base page and may also provide links to popular content or related content on your site. Google provides a 404 widget that you can embed in a 404 page to auto-combine with many useful features. You can also use Google Webmaster Tools to find the source of the URL that's showing the "not found" error message.
Avoid:
- Allows your 404 page to be indexed in search engines (make sure your webmaster is configured to provide an HTTP 404 status code if a non-existent page is requested)
- Provides only fuzzy messages like "Not found", "404", or no 404 page at all
- Use a design for your 404 page that is inconsistent with the rest of your site.
Conclusion
In our guide to improving a good website structure, we've tried to give you a step-by-step approach that you can apply to your website to improve user flow across your site. Over time, this strategy will generate SEO benefits for your content and, just as importantly, drive people to the most important content on your website.
Keep in mind that the strategies we outline here must be incorporated into how you manage your website. Every six months, you should review how people are using your site. Ensuring that your website structure is easy to navigate and your content relevant is a surefire way to increase your revenue.
Thus the post about Improving a Good Website Structure. Hopefully this article is useful and can help you. Let's share this article to help other friends. Thank You!

.jpg)




